COP30's Tripling Pledge: Momentum Meets Implementation Challenge
COP30’s arguably flagship outcome: a call to triple global adaptation finance by 2035, marked what UN Secretary-General Guterres called "a true turning point" for adaptation to be recognised as critical global action. Nearly 200 countries agreed on 59 voluntary indicators for the Global Goal on Adaptation, with each nation supposed to tailor implementation to its community needs and resilience priorities. UN Foundation's Cristina Rumbaitis del Rio stressed the importance of sustained attention to implementation alongside indicator refinement, noting that while imperfect, the 59 indicators represent critical progress that the global community "could not afford to wait any longer" to establish, with youth-led movements providing the urgency and passion driving adaptation's ascent on diplomatic agendas.
AI Guidance Helps Indian Farmers Navigate Erratic Monsoons, Yet Access Gaps Persist
Indian smallholder farmers increasingly adopt AI-powered agricultural apps—Fasal, KisanGPT, BharatAgri, KrishiMunni—that deliver hyperlocal weather forecasts, soil health data, and pest alerts, helping navigate increasingly unpredictable climate patterns. Sugarcane farmer Yuvraj Mohite credited the Fasal app with saving 80 tonnes of crop during destructive June monsoon rains, with improved water and fertiliser efficiency reducing costs and improving quality. The Gates Foundation's $1.4 billion commitment targets scaling such tools through AIM for Scale, which designs cost-effective digital solutions for South Asian and sub-Saharan African smallholders, with app downloads surging 19% from 99 million in 2023 to 118 million in 2024. Upgrading India's monsoon forecasts to global average accuracy alone could generate $3 billion in benefits over five years at under $6 million cost.

Asia's Urban Adaptation Crisis: $1.7 Trillion Need Meets Investor Caution
Asian Development Bank estimates that developing Asia's cities require $1.7 trillion annually through 2030 for climate-resilient infrastructure, yet governance fragmentation, data transparency gaps, and unpredictable financial returns deter private capital, which currently comprises barely 3% of global adaptation financing. Cheong-Chua Koon Hean, chair of Singapore's Lee Kuan Yew Centre for Innovative Cities, highlighted overlapping national, provincial, and local governance structures, creating uncertainty for investors seeking long-term planning consistency. CapitaLand's Vinamra Srivastava noted that adaptation projects often lack predictable cash flows and quantifiable returns. Meanwhile, Southeast Asia needs $210 billion annually for adaptation yet receives only $2.5 billion in external finance, with Manila, Bangkok, and Jakarta facing critical capital shortages for water, sanitation, green infrastructure, and renewable energy projects.
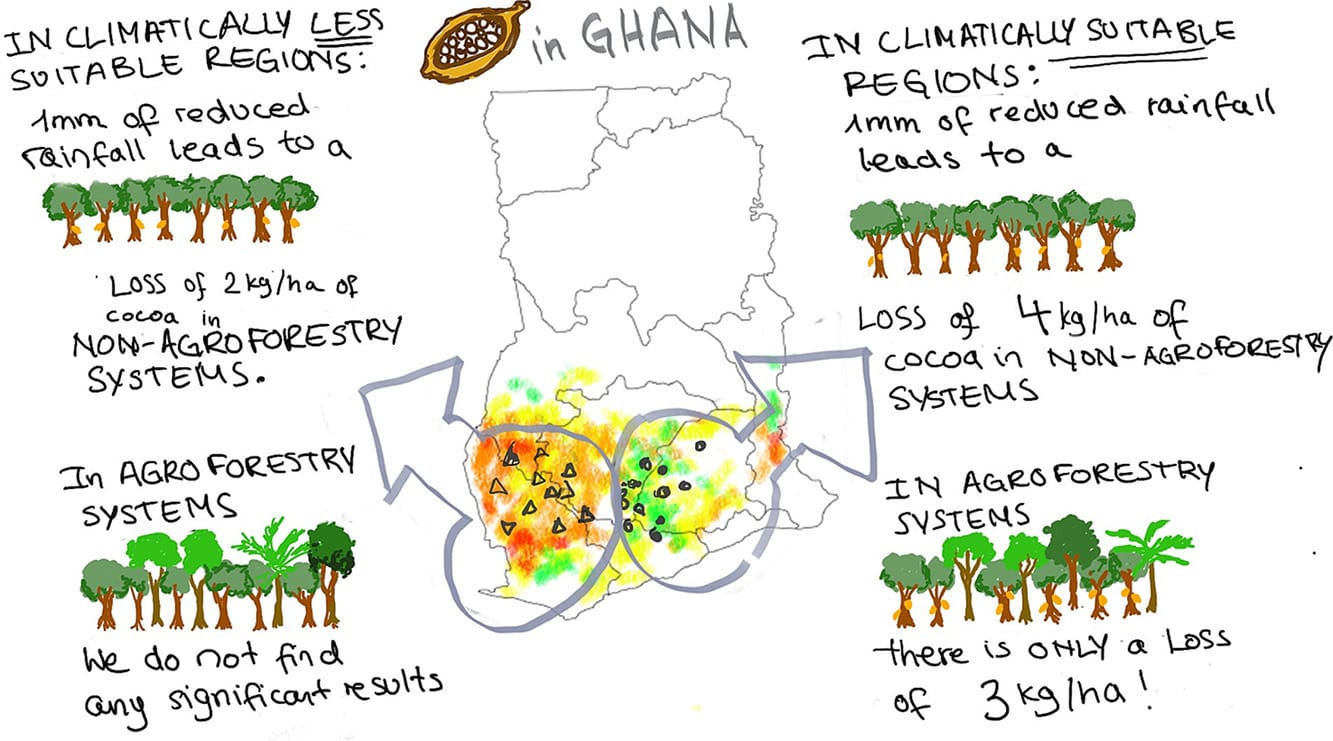
Agroforestry for Cocoa: Climate Solutions Require Hyperlocal Tailoring
University of Göttingen and European Commission research reveals that Ghanaian cocoa farmers practising agroforestry—cultivating under shade trees—withstand reduced rainfall better than conventional growers, but benefits depend critically on local climate conditions. In Ghana's wetter regions, agroforestry significantly buffers yield losses during drought; in drier areas, however, shade trees compete with cocoa for scarce soil moisture, offsetting protective benefits, particularly where shallow-rooted species like avocado intensify water competition. The findings, based on 365 households across 44 villages and satellite rainfall data, underscore that adaptation strategies cannot be uniformly prescribed, but require tailoring to regional climate zones. Researchers emphasise that in increasingly arid areas where cocoa production becomes unviable, transitioning to drought-tolerant alternatives like cashew nuts should be considered.
Sequencing of 1,000 Butterfly Genomes Unlock Evolutionary Resilience Insights
Wellcome Sanger Institute and international collaborators reached a milestone, sequencing 1,000 butterfly and moth species as part of Project Psyche, an initiative aiming to decode all 11,665 European Lepidoptera species to understand evolutionary resilience and climate adaptation. Butterflies and moths—comprising 10% of known eukaryotic species—are key ecosystem pollinators, food chain components, and biodiversity indicators reacting quickly to environmental change; genomic analysis revealed that their chromosomes have remained largely unchanged over 230 million years despite dramatic evolutionary diversification. Reference genomes enable researchers to compare extinct, declining, and stable populations to understand climate and human activity impacts on insect diversity. With insect populations declining 65% in the UK since 2021, understanding genetic signatures of resilient species could inform protection strategies for other vulnerable fauna.
Know someone interested in adapting to a warmer world? Share Liveable with someone who should be in the know.
Or copy and paste this link to share with others: https://research.liveable.world/subscribe
